| | Business linesProperty and casualty insurancePremium development
|
Premium volume written in property and casualty insurance |
 |
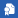
In property and casualty insurance, the UNIQA Group was able to continue the extremely positive developments of the previous year again in 2008, increasing the premiums written by 9.3% to €2,401 million (2007: €2,198 million). Despite the continued intense competition, the premium volume in Austria rose by 2.1% to €1,294 million (2007: €1,268 million). In the Central and Eastern European regions (CEE & EEM), the considerably more rapid growth also continued in 2008. The premiums written grew by 33.1% to €702 million (2007: €528 million), thereby contributing 29.2% (2007: 24.0%) to the Group premiums in property and casualty insurance. In the Western European markets, however, only moderate growth was experienced in 2008. Here, the premiums written increased slightly by 0.8% to €405 million (2007: €402 million). Overall, the international share of Group premiums in this segment amounted to 46.1% (2007: 42.3%).
Details on the premium volume written in the most important risk classes can be found in the Group notes (cf. Group notes No. 31).
The retained premiums earned (according to IFRS) in casualty and property insurance totalled €2,214 million at the end of the year (2007: €1,858 million) – representing a major increase of 19.1%.
| Premiums written |
2,401 |
2,198 |
2,037 |
1,934 |
1,656 |
| Share CEE & EEM |
29.2% |
24.0% |
21.0% |
18.7% |
18.6% |
| Share WEM |
16.9% |
18.3% |
18.5% |
19.6% |
13.4% |
| International share |
46.1% |
42.3% |
39.4% |
38.3% |
32.0% |
| Premiums earned (net) |
2,214 |
1,858 |
1,716 |
1,628 |
1,394 |
| Net investment income |
42 |
258 |
141 |
131 |
89 |
| Insurance benefits |
–1.412 |
-1,251 |
-1.130 |
-1,106 |
-908 |
| Net loss ratio (after reinsurance) |
63.8% |
67.3% |
65.9% |
68.0% |
65.1% |
| Gross loss ratio (before reinsurance) |
62.2% |
67.9% |
64.1% |
66.4% |
63.6% |
Operating expenses less
reinsurance commissions |
–740 |
-606 |
-569 |
-553 |
-479 |
| Cost ratio (after reinsurance) |
33.4% |
32.6% |
33.2% |
34.0% |
34.4% |
| Net combined ratio (after reinsurance) |
97.2% |
99.9% |
99.0% |
101.9% |
99.5% |
| Gross combined ratio (before reinsurance) |
94.2% |
98.7% |
95.4% |
98.2% |
95.8% |
| Profit on ordinary activities |
113 |
238 |
129 |
81 |
59 |
| Net profit |
104 |
193 |
104 |
54 |
53 |
Developments in insurance benefits
The total retained insurance benefits rose in 2008 by 12.8% to €1,412 million (2007: €1,251 million), which represents a disproportionately high increase relative to the increase in premiums. Insurance benefits increased in Austria by 5.7% to €808 million (2007: €765 million) and in Western European countries (WEM) by 15.3% to €248 million (2007: €215 million). In the Central and Eastern European regions (CEE & EEM), the insurance benefits increased in line with the increased premium volume by 31.0% to €356 million (2007: €272 million).
As a result of this development, the net loss ratio (retained insurance benefits relative to premiums earned) fell by 3.5 percentage points to 63.8% (2007: 67.3%). At the end of 2008, the gross loss ratio (before reinsurance) was even lower at 62.2% (2007: 67.9%). In Austria, the net loss ratio for the past financial year fell to 65.3% (2007: 70.2%) and in Western Europe to 69.2% (2007: 73.1%), while in the CEE & EEM regions it remained stable at 57.7% (2007: 57.3%).
Operating expenses, combined ratio
Total operating expenses in property and casualty insurance less reinsurance commissions and profit shares from reinsurance business ceded rose by 22.2% to €740 million (2007: €606 million). In the process, acquisition costs rose by 11.5% to €497 million (2007: €445 million), which was a disproportionately low increase compared with the rise in premiums, while other operating expenses increased by 52.0% to €244 million (2007: €160 million) due to lower retained reinsurance commissions.
The cost ratio in property and casualty insurance therefore increased slightly in the past financial year to 33.4% (2007: 32.6%). The net combined ratio fell due to the excellent loss ratio and lay significantly below 100% in 2008 at 97.2% (2007: 99.9%). The combined ratio before reinsurance fell even further to reach 94.2% (2007: 98.7%).
Investment results
Net income from investments less financing costs decreased in the past financial year by 83.7% to €42 million (2007: €258 million). The capital investments in property and casualty insurance declined by 7.7% to €3,315 million (2007: €3,590 million).
Profit on ordinary activities, net profit
Profit on ordinary activities in property and casualty insurance fell in 2008 by 52.4% to €113 million (2007: €238 million). Net profit was also down by 45.9% to €104 million (2007: €193 million). Health insurancePremium development
Premium volume written in health insurance |
|
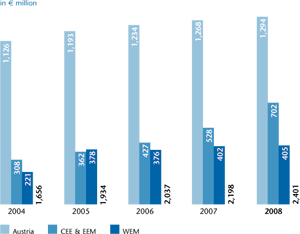
In comparison to the previous year, premiums written in health insurance increased
by 4.4% to €948 million (2007: €908 million). In Austria, where UNIQA
is the market leader in health insurance, the premium volume in 2008 grew over
the previous year by 3.3% to reach €748 million (2007: €724 million). In the
WEM region, the premiums written increased by as much as 6.4% to €191 million
(2007: €180 million). In the countries of Eastern and South Eastern Europe,
private health insurance continued to play a subordinate role with a premium
volume of €8 million (2007: €4 million). Overall, the international share in the
total health insurance premiums in 2008 was 21.1% (2007: 20.3%).
In 2008, the retained premiums earned (according to IFRS) in health insurance
totalled €946 million at the end of the year (2007: €906 million), amounting
to an increase of 4.5%.
| Premiums written |
948 |
908 |
890 |
845 |
745 |
| International share |
21.1% |
20.3% |
20.5% |
17.9% |
9.6% |
| Premiums earned (net) |
946 |
906 |
887 |
849 |
742 |
| Net investment income |
14 |
134 |
114 |
101 |
81 |
| Insurance benefits |
–822 |
-811 |
-806 |
-773 |
-675 |
Acquisition expenses less
reinsurance commissions |
–134 |
-129 |
-137 |
-131 |
-119 |
| Cost ratio (net after reinsurance) |
14.2% |
14.3% |
15.4% |
15.4% |
16.1% |
| Profit on ordinary activities |
3 |
96 |
54 |
41 |
23 |
| Net profit |
–1 |
72 |
35 |
35 |
20 |
Developments in insurance benefits
Despite the increased business volume, insurance benefits only rose
slightly by 1.3% to €822 million (2007: €811 million). This also lowered
the benefits
ratio after reinsurance to 86.9% (2007: 89.6%). In Austria,
insurance
benefits even decreased by 1.1% to €641 million (2007: €649
million). In the international markets, the insurance benefits in 2008
increased
by 11.1% to reach €181 million at the end of the year (2007:
€163 million).
Operating expenses
Total operating expenses in health insurance less reinsurance commissions
and profit shares from reinsurance business ceded rose in 2008 by 3.8%
to €134 million (2007: €129 million), a disproportionately low increase
compared
with the premium volume. Despite the increased premium
volume,
acquisition expenses rose only slightly by 0.8% to €87 million
(2007: €86 million). Other operating expenses increased by 10.0% to €47
million (2007: €43 million). As a result of this development, the cost ratio
in health insurance decreased further in 2008 to 14.2% (2007: 14.3%).
Investment results
Net income from investments less financing costs fell by 89.7% to €14
million
(2007: €134 million). In the health insurance segment, capital
investments
grew by 9.6% to €2,288 million (2007: €2,087 million).
Profit on ordinary activities, net profit
Profit on ordinary activities in health insurance fell in the reporting year due to
the negative capital market environment by 96.4% to €3 million (2007: €96
million). Net profit declined in 2008 to €–1 million (2007: €72 million).
Life insurance Premium development
International premium volume written in life insurance |
|
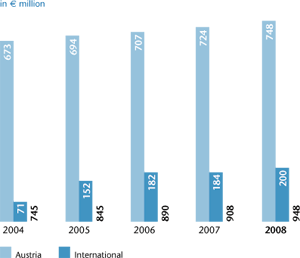
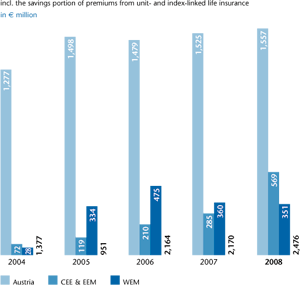
The life insurance premium volume written, including the savings portion of
unit- and index-linked life insurance, increased in 2008 by 14.1% to €2,476
million (2007: €2,170 million). Revenues from policies with recurring premium
payments rose by 4.4% to €1,563 million (2007: €1,497 million).
In the single premium business, premiums in the area of unit-linked life
insurance decreased by 9.6% to €408 million (2007: €452 million), while
classic single-premium policies climbed by 128.3% to €505 million (2007:
€221 million). Overall, the single premium business grew by 35.7% to
€913 million (2007: €673 million).
Although the premium development in Austria was still encumbered in
2008 by the loss of premium income from contracts with reduced payment
terms, the premium volume still rose by 2.1% to €1,557 million (2007:
€1,525 million) due to the continued growth in unit-linked life insurance
products. Revenues from policies with recurring premium payments rose
by 2.8% to €1,321 million (2007: €1,285 million). The single premium
business remained roughly at the level of the previous year at €236 million
(2007: €241 million). The Group companies in the Central and Eastern
European regions (CEE & EEM) experienced growth in the life insurance
segment that was many times stronger. The premium volume written
including
the savings portion of unit- and index-linked life insurance doubled
to €569 million (2007: €285 million). The share of life insurance from
these countries thus already amounted to 23.0% in 2008 (2007: 13.1%).
In the Western European countries (WEM), on the other hand, the premium
volume
written declined slightly by 2.7% to €351 million (2007: €360
million). Overall, the Western European region (WEM) contributed 14.2%
(2007: 16.6%) to the total life insurance premiums of the Group.
The risk premium share of unit- and index-linked life insurance included
in the consolidated financial statements totalled €97 million in 2008
(2007: €86 million). The savings portion of the unit- and index-linked life
insurance
lines amounted to €823 million (2007: €748 million) and was,
in accordance
with FAS 97 (US-GAAP), balanced out by the changes in
the actuarial provision.
Including the savings portion of the unit- and index-linked life insurance
(after reinsurance) in the amount of €774 million (2007: €695 million),
the premiums earned in life insurance rose by 15.1% to €2,344 million
(2007: €2,037 million). The retained premiums earned (according to IFRS)
increased in 2008 by 17.0% to €1,570 million (2007: €1,342 million).
| Premiums written |
1,653 |
1,422 |
1,605 |
1,591 |
1,199 |
Savings portion of premiums from
unit- and index-linked life insurance |
823 |
748 |
559 |
360 |
178 |
Premiums written incl. savings portion
of premiums from unit- and index-linked
life insurance |
2,476 |
2,170 |
2,164 |
1,951 |
1,377 |
| Share CEE & EEM |
23.0% |
13.1% |
9.7% |
6.1% |
5.2% |
| Share WEM |
14.2% |
-16.6% |
22.0% |
17.1% |
2.1% |
| International share |
37.1% |
29.7% |
31.7% |
23.2% |
7.3% |
| Premiums earned (net) |
1,570 |
1,342 |
1,527 |
1,523 |
1,166 |
Savings portion of premiums from
unit- and index-linked life insurance
(net after reinsurance) |
774 |
695 |
499 |
311 |
129 |
Premiums earned (net) incl. the savings
portion of premiums from unit- and
index-linked life insurance |
2,344 |
2,037 |
2,027 |
1,834 |
1,295 |
| Net investment income |
133 |
563 |
610 |
731 |
580 |
| Insurance benefits |
–1,328 |
-1,534 |
-1,780 |
-1,898 |
-1,451 |
Operating expenses less reinsurance
commissions and change in deferred
acquisition costs |
–347 |
-328 |
-304 |
-284 |
-253 |
| Cost ratio |
14.8% |
16.1% |
15.0% |
15.5% |
19.6% |
Other operating expenses less
insurance commissions |
–363 |
-321 |
-261 |
-244 |
-231 |
| Cost ratio (net after reinsurance) |
15.5% |
15.7% |
12.9% |
13.3% |
17.8% |
| Profit on ordinary activities |
–27 |
5 |
56 |
69 |
39 |
| Net profit |
–37 |
4 |
37 |
44 |
29 |
Developments in insurance benefits
The retained insurance benefits decreased in the reporting period by 13.5%
to €1,328 million (2007: €1,534 million). In Austria, insurance benefits
also decreased by 36.8% to €838 million (2007: €1,326 million). In the
Western European region (WEM), insurance benefits decreased by 11.4% to
€105 million (2007: €118 million), while they rose in Central and Eastern
Europe (CEE & EEM) by 325.2% to €385 million (2007: €91 million) due
to the strong premium growth.
Operating expenses
Total operating expenses in life insurance less reinsurance commissions
and profit shares from reinsurance business ceded rose in 2008 by 13.1%
to €363 million (2007: €321 million). Acquisition expenses rose by 9.2%
to €286 million (2007: €262 million). In line with the extremely positive
development
of new business, an increase in expenses due to the change
in deferred acquisition costs was observed again in 2008 in the amount of
€23 million. Because the reinsurance commissions received also declined
to €6 million (2007: €11 million), among other factors, other operating
expenses increased by 30.8% to €76 million (2007: €58 million). However,
since the premium volume in life insurance developed even more rapidly,
the cost ratio, i.e. the ratio of all claims incurred to the Group premiums
earned, including
the savings portion of unit- and index-linked life insurance,
declined to 15.5% (2007: 15.7%). Adjusted for the change in deferred
acquisition costs, the cost ratio even declined to 14.8% in 2008 (2007:
16.1%).
Investment results
The net income from investments less financing costs declined in the
reporting
year by 76.4% to €133 million (2007: €563 million) due to
consequences of the financial crisis. The capital investments including the
investments for unit- and index-linked life insurance shrank slightly in 2008
by 0.8% to €15,739 million (2007: €15,867 million).
Profit on ordinary activities, net profit
The profit on ordinary activities in life insurance was negative in 2008 due to the
negative capital markets environment, and amounted to €–27 million (2007: €5
million). The net profit was also negative at €–37 million (2007: €4 million).
|
| | |

 Group Management Report
Group Management Report Business lines
Business lines




 Contact
Contact